Data Science: Introduction¶
Goal¶
- insight from data
Fab Futures¶
- introductions
fab labs¶
Fab Academy¶
Academany¶
FAB23¶
21st-century vocational skills¶
- immediately applicable skills addressing local needs
format¶
- rotating one-month hands-on immersions
- 30 minute review, 60 minute interactive lectures
- videoconference etiquette
- student notebooks
- credit all sources used (including AI prompts), otherwise it's plagiarism
- document as you do
- assignment evaluation
- completion certification
- train trainers
- diploma cycle
- open content
goals¶
- familiarity with concepts
- ability to do sample applications
- directions for further study
schedule¶
Examples¶
John Snow (1854)¶
Florence Nightingale (1863)¶
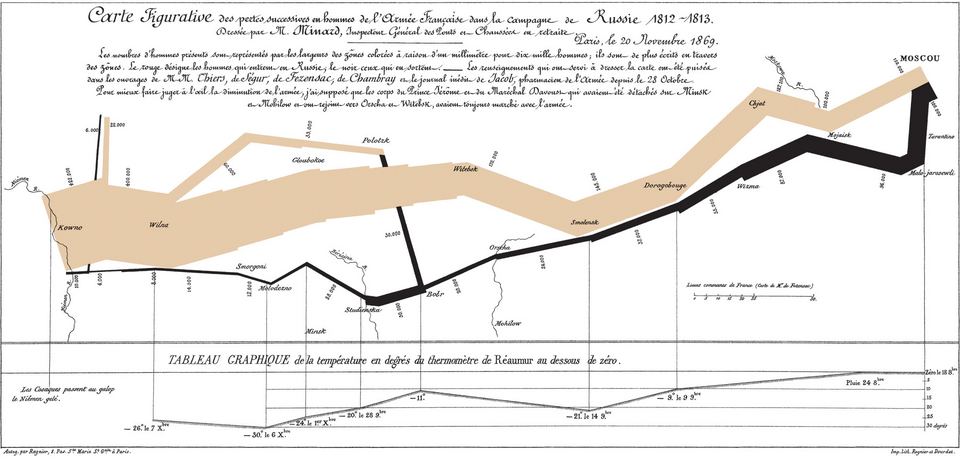
Charles Joseph Minard (1869)¶
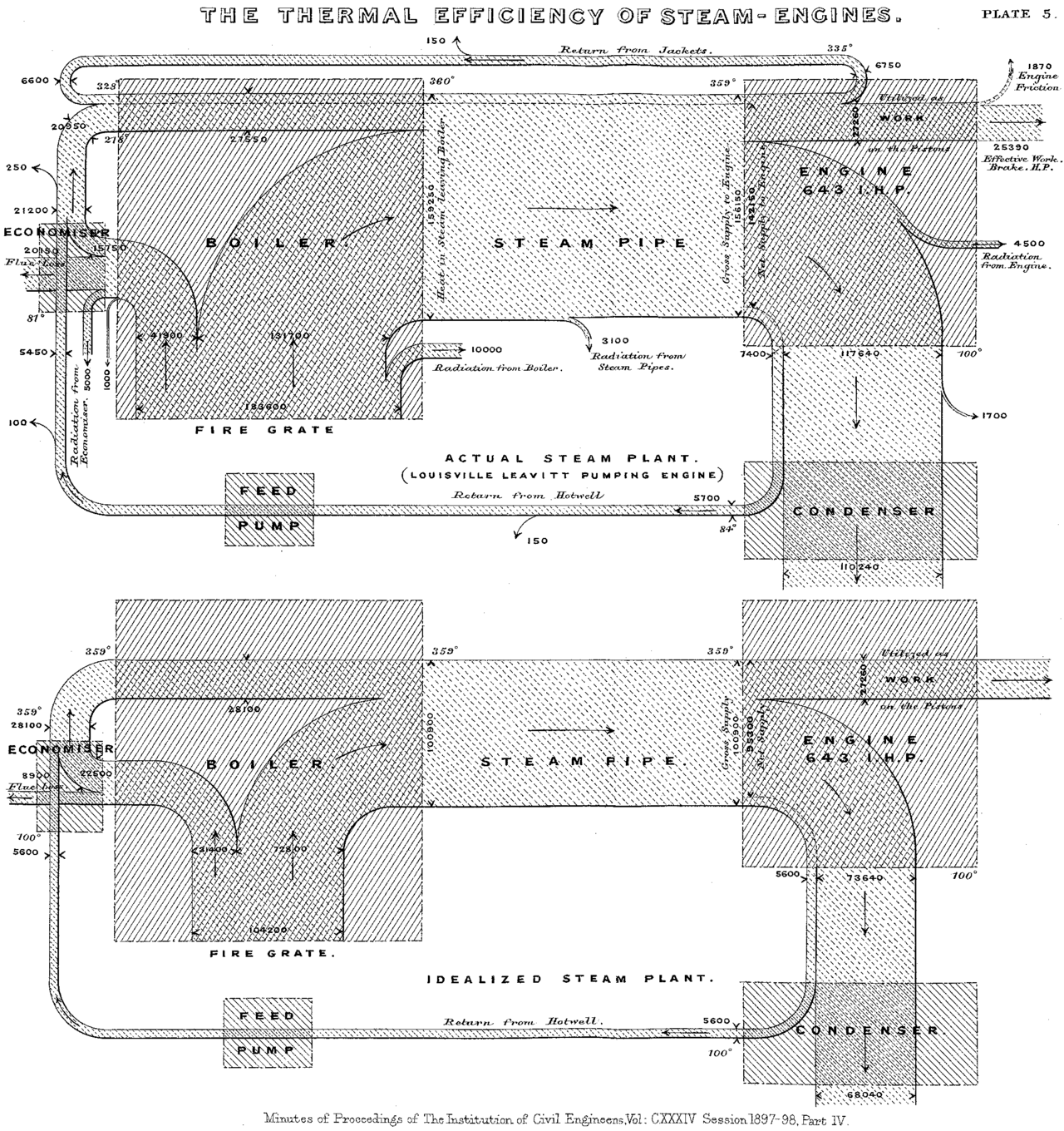
Captain Matthew Henry Phineas Riall Sankey (1898)¶
Edward Tufte (1983)¶
Santa Fe Institute (1993)¶
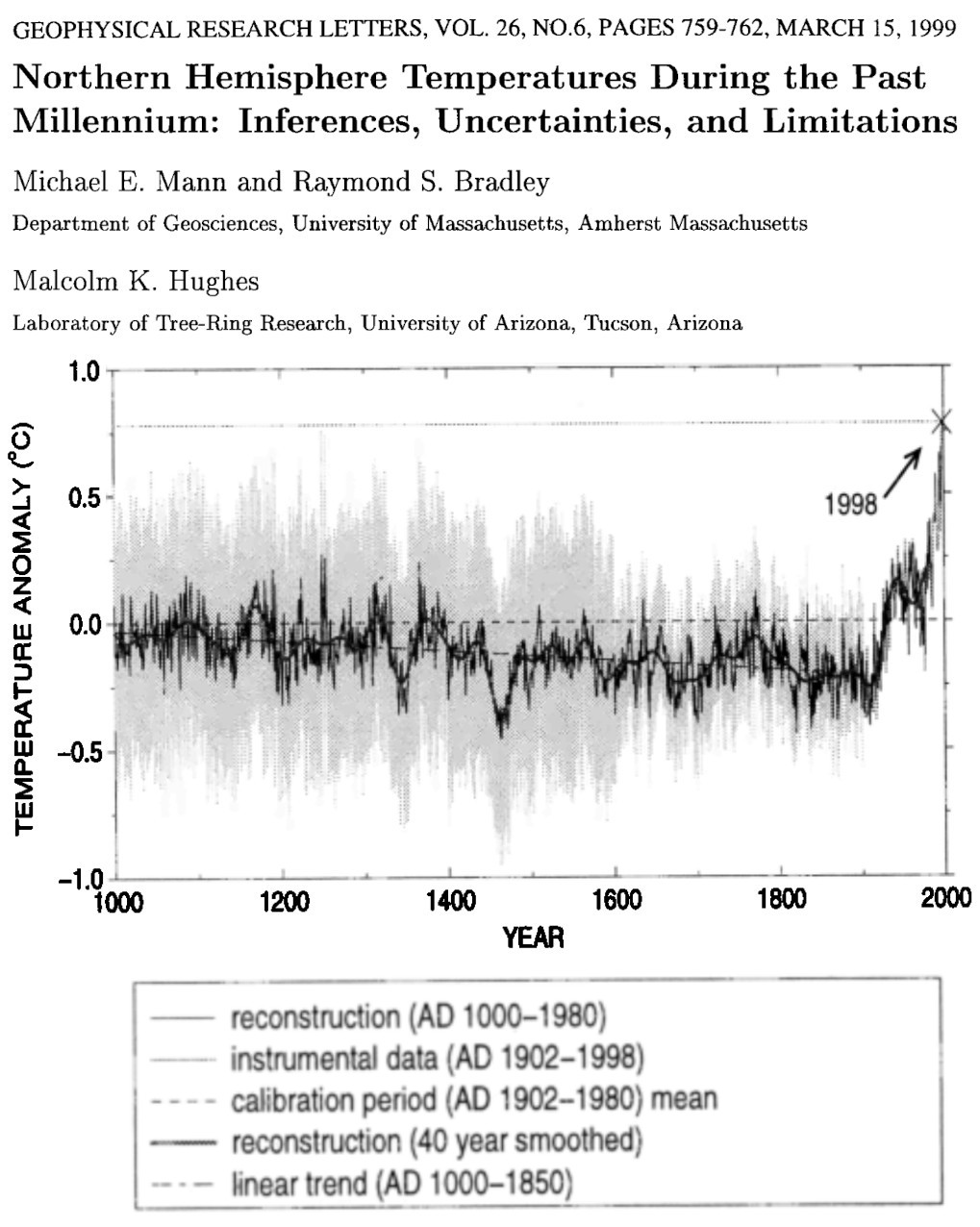
Michael Mann et al. (1999)¶
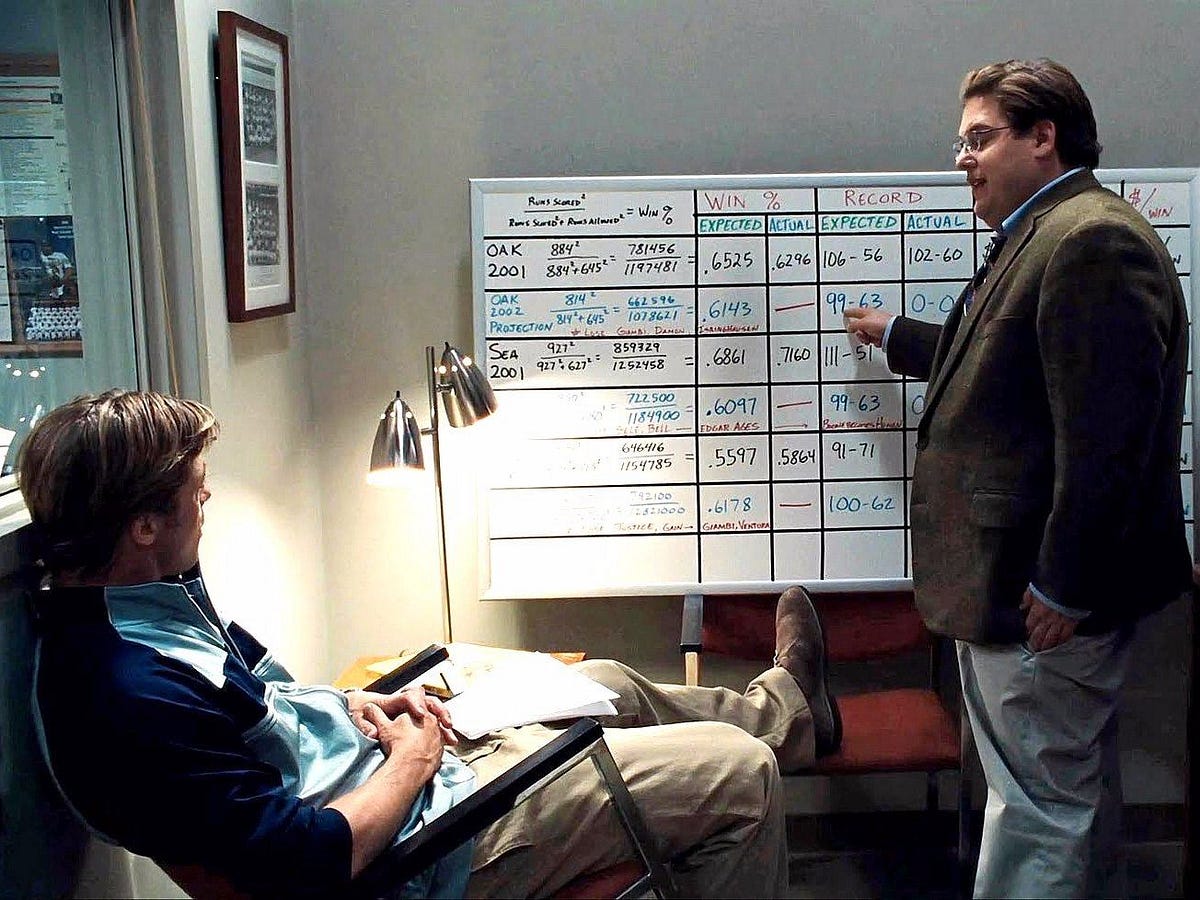
Moneyball (2011)¶
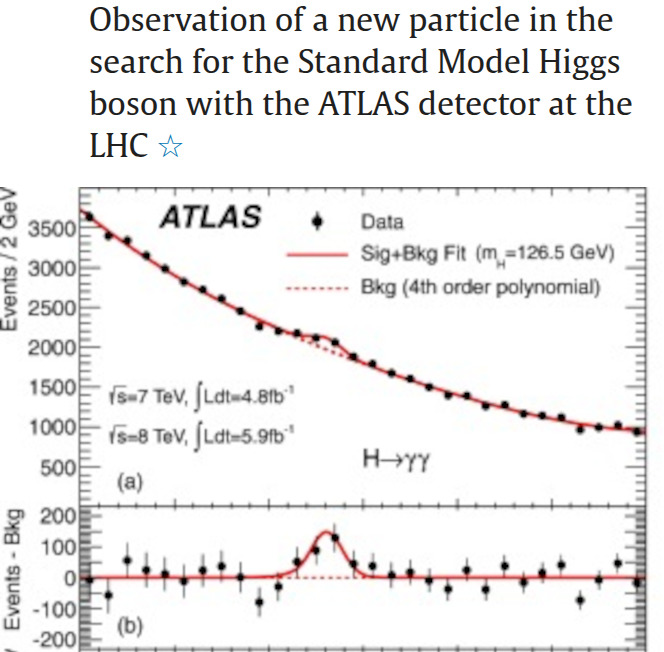
LHC (2012)¶
Otherlab (2018)¶
Nadieh Bremer (2025)¶
Sports Analytics (2026)¶
Taxonomy¶
data are plural¶
- singular is datum, or data point
types¶
- regression: fitting a continuous function
- classification: assigning data to discrete categories
uses¶
- interpolation: filling in points within a data set
- extrapolation: projecting points outside of a data set
- classification: assigning categories in a data set
- detection: identifying events in a data set
- smoothing: reducing noise in a data set
parameters¶
- parametric: fitting a function to data with meaningful parameters
- non-parametric: fitting a function to data with parameters whose values are not meaningful
- hyperparameters: variables that determine model architecture and training before fitting
learning¶
- supervised: labeled data with an input-output relationship
- unsupervised: finding structure in unlabeled data
- reinforcement: maximizing return in e.g. games, finance
modeling¶
- training: developing a model
- inference: using a model
data analysis¶
- offline: data analyzed after it is collected
- online: data analyzed in real time
- big data: data sets that are beyond the capacity of conventional systems
Resources¶
- The Nature of Mathematical Modeling
- Numerical Recipes
- Jupyter
- data sets
- principles
Assignment¶
- Select and document a data set to analyze
- Connect to a JupyterLab server and become familiar with the user interface
Review¶
(c) Neil Gershenfeld for Fab Futures, 12/14/25